Automatización de WhatsApp con Python
- Cómo trabajar con la API de WhatsApp usando Python;
- Integración con Whapi.Cloud para automatizar varias tareas;
- Uso de webhooks para gestionar y responder automáticamente a los mensajes;
- Conectar tu bot de WhatsApp con ChatGPT para conversaciones impulsadas por IA;
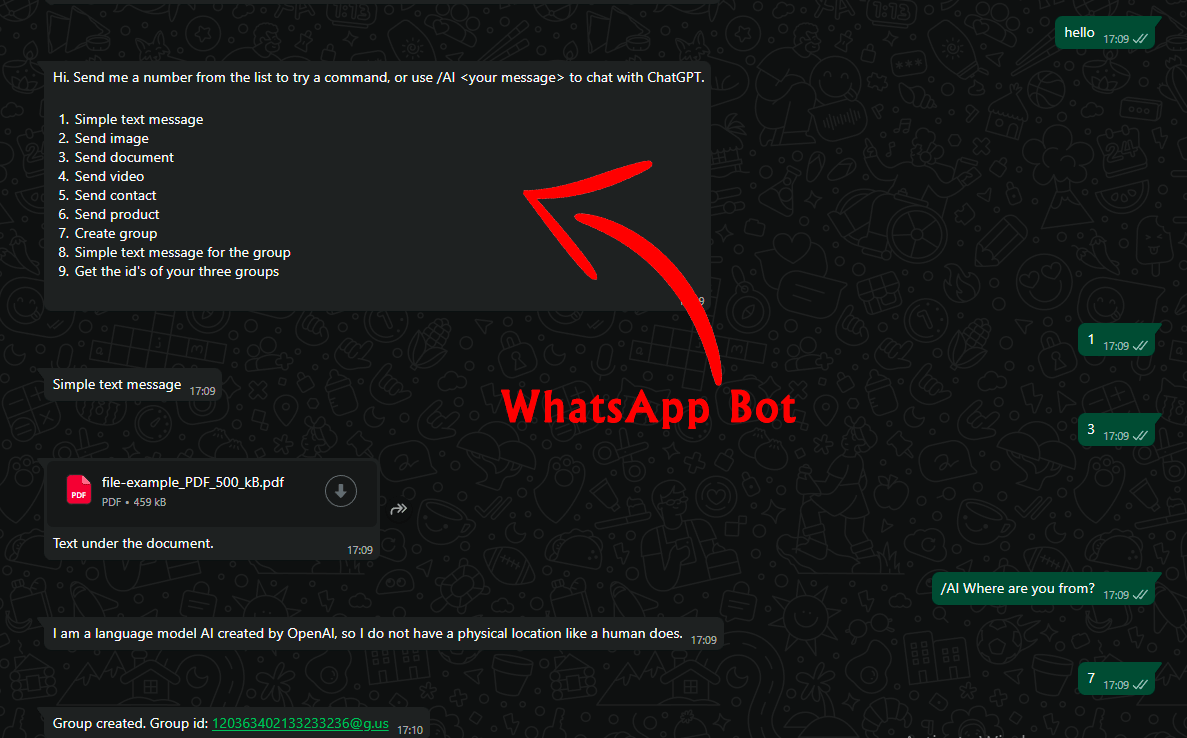
Para facilitar el trabajo, puede utilizar nuestros scripts de bots en Python, que hemos publicado en GitHub. Estos proyectos describen en detalle el proceso de configuración y prueba, y dentro del código encontrará comentarios útiles. Es un excelente punto de partida para desarrolladores principiantes.
Preparación para desarrollar un bot
- Python. Instale Python si aún no lo tiene. Descargue la última versión (se recomienda 3.6 o superior) desde el sitio oficial y siga las instrucciones.
- Flask. Flask es un framework web ligero en Python que usaremos para configurar el servidor y manejar los webhooks. Puede instalar Flask con el siguiente comando: pip install Flask
- Token de API. Regístrese en Whapi.Cloud para obtener un token de API. Este token permitirá que su bot interactúe con WhatsApp a través de la API. Después de registrarse, se le proporcionará un canal gratuito con algunas limitaciones, suficiente para probar su desarrollo. Whapi.Cloud es un proveedor que destaca por su estabilidad, bajo costo y amplia funcionalidad. A continuación, se ofrecen instrucciones para obtener el token.
- Webhook configurado. Para que el bot pueda manejar mensajes entrantes y eventos de WhatsApp, necesitará la URL de su servidor (local o externo) para procesar las notificaciones de WhatsApp. En este artículo explicaremos en detalle cómo hacerlo y dónde obtener dicho enlace.
Obteniendo el token para la API de WhatsApp
Registro y conexión de número
- 1. Vaya al panel y abra la página del canal Default Channel, que ya está creado para usted.
- 2. En el primer paso, verá un código QR con instrucciones.
- 3. Abra WhatsApp en su dispositivo, vaya a Configuración → Dispositivos vinculados → Vincular dispositivo → Escanear código QR.
- 4. Después de conectarse exitosamente, asigne un nombre al canal (por ejemplo, "Mi Chatbot") para facilitar su uso en el futuro.
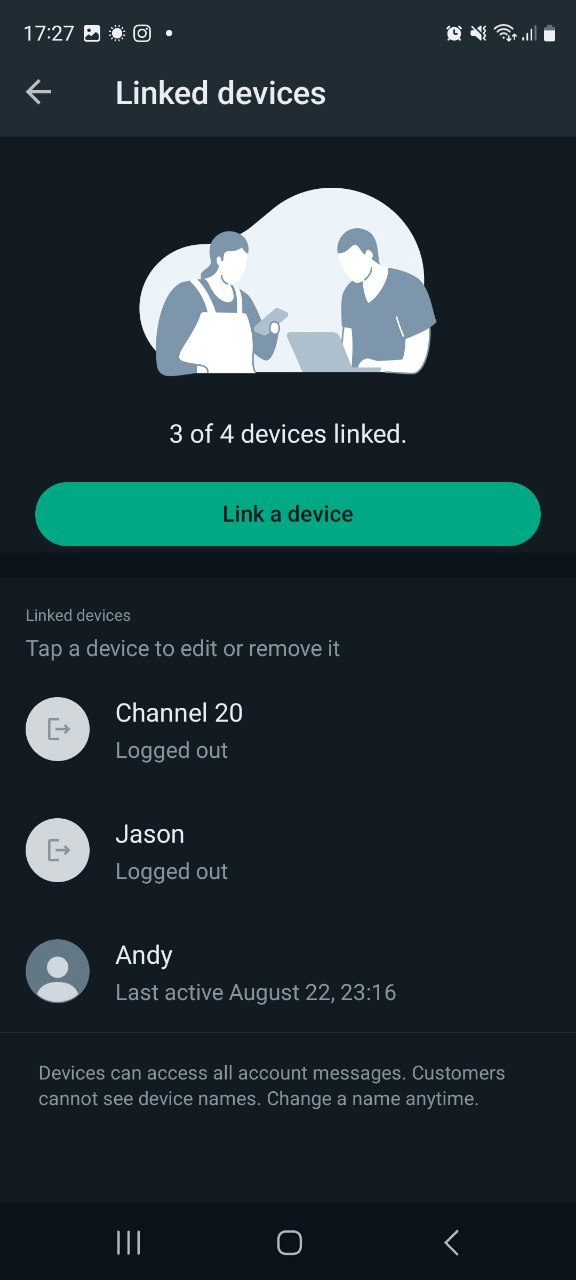
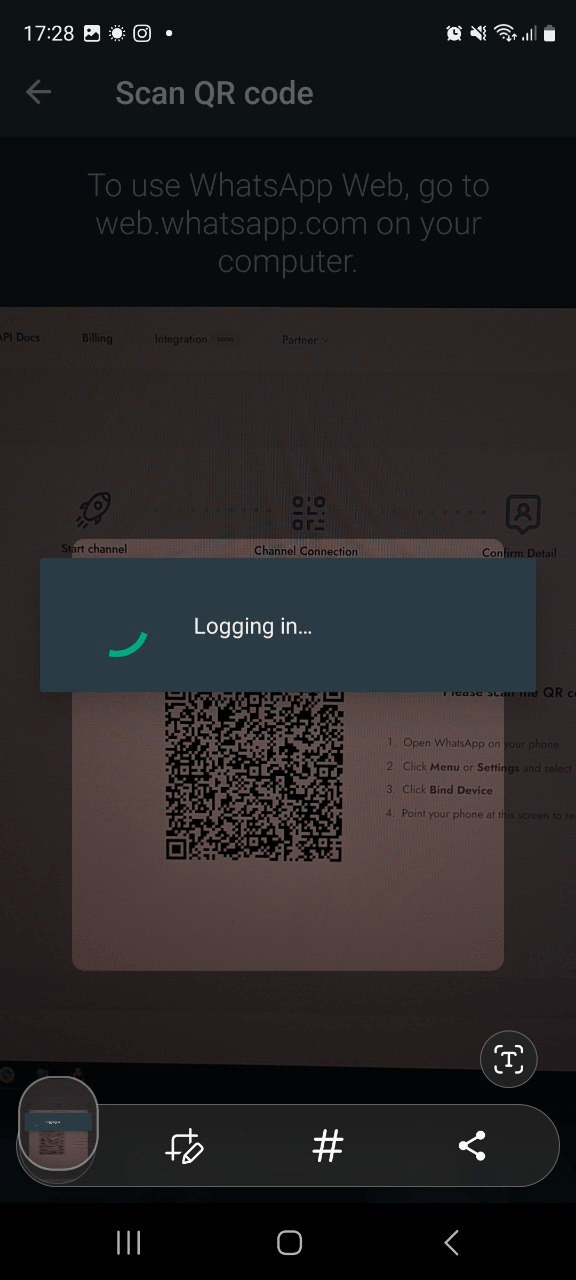
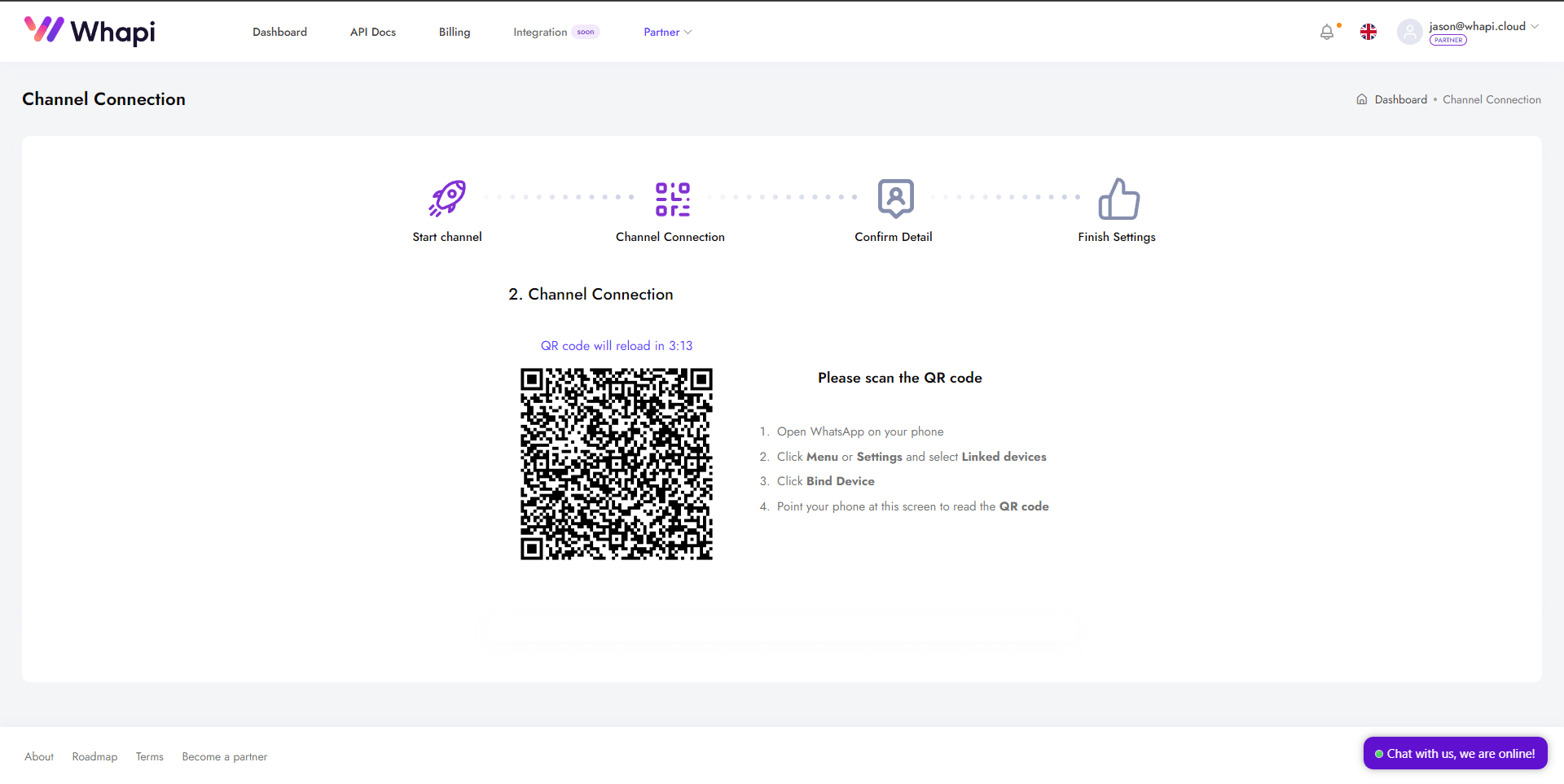
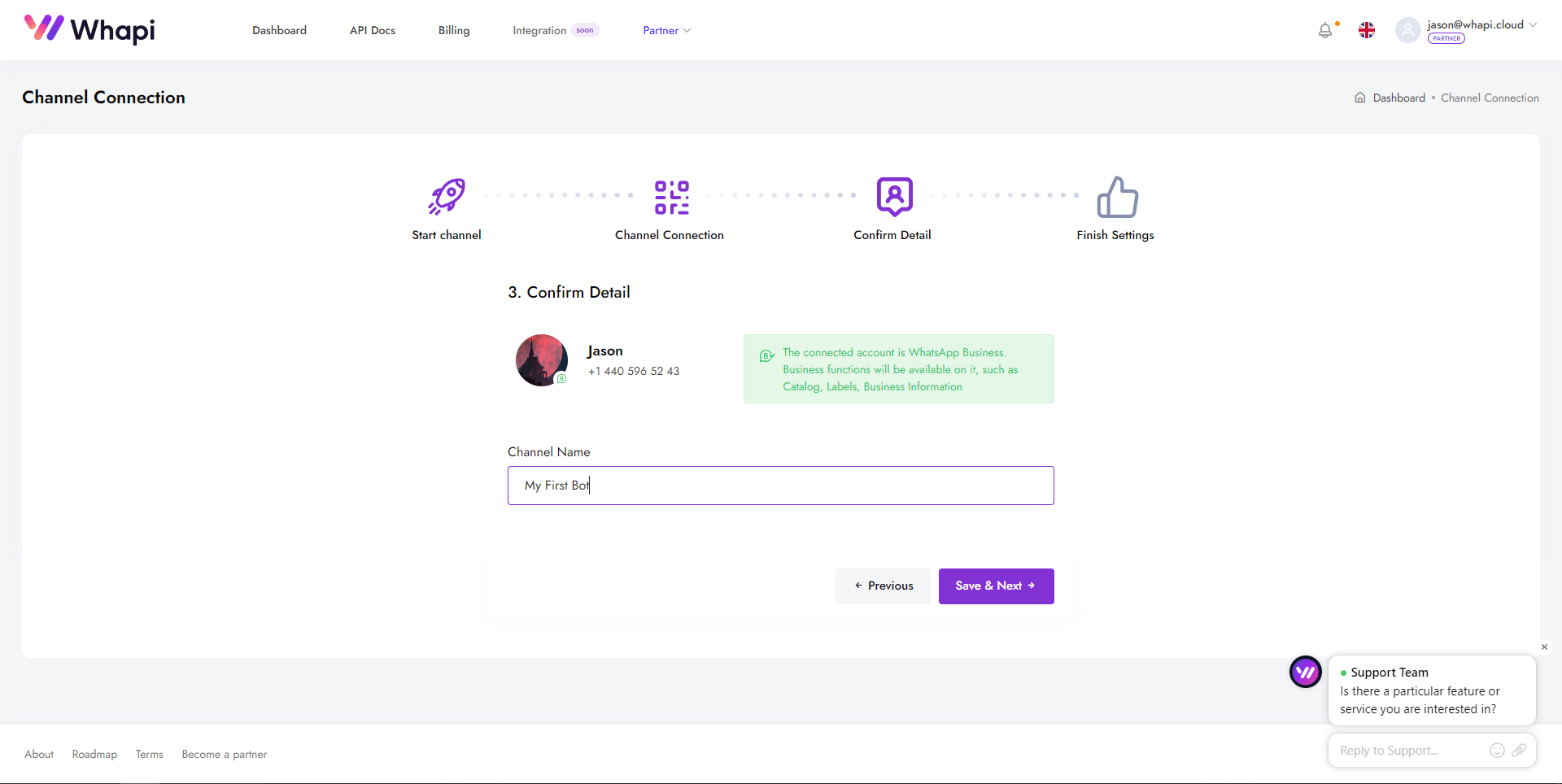
Obtención del token de API
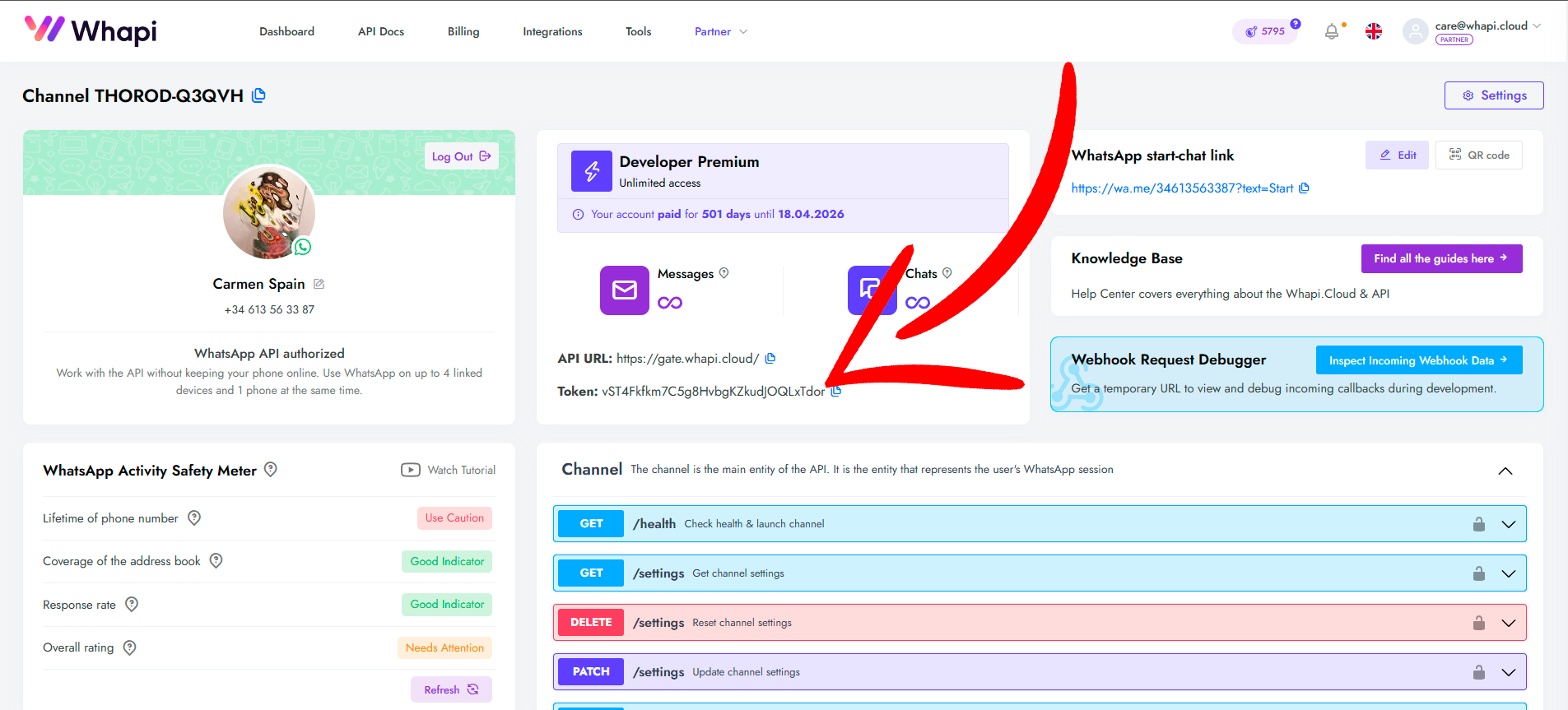 Your API Key
Your API Key
Herramientas para trabajar con la API
- Hub práctico para desarrolladores: Plataforma especializada con documentación y ejemplos que le permitirá obtener fragmentos de código para todos los endpoints en varios lenguajes de programación.
- Colección de Postman: Solicitudes preparadas para probar la API a través de Postman.
- Archivo Swagger: Descripción detallada de todos los métodos de la API, con la posibilidad de realizar pruebas directamente desde la página del canal.
¿Qué es un Webhook y cómo configurarlo?
¿Qué es un webhook?
- Notificaciones instantáneas. Todos los eventos se procesan casi en tiempo real.
- Alta capacidad. La velocidad de recepción de notificaciones está limitada únicamente por el rendimiento de su servidor.
- Flexibilidad. Puede recibir solo los eventos que realmente necesita, como: Mensajes personales; Mensajes en grupos; Cambios en el estado de los mensajes; Cambios en los participantes de los grupos; Notificaciones de llamadas perdidas; Estados de los canales y mucho más.
¿Cómo y dónde obtener una URL para el webhook?
- 1) Descargue Ngrok desde su sitio oficial y descomprímalo. Luego, abra el terminal y navegue a la carpeta donde está almacenado Ngrok.
- 2) Ejecute ./ngrok http PUERTO, reemplazando PUERTO por el puerto en el que su servidor Flask está funcionando localmente (por ejemplo, 80).
- 3) Ahora tendrá una URL pública que puede usar como URL del webhook. Cópiela para su uso posterior.
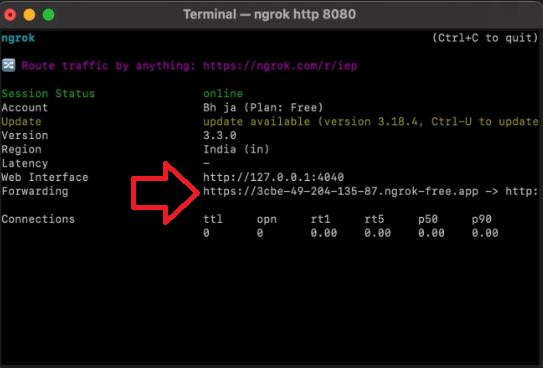
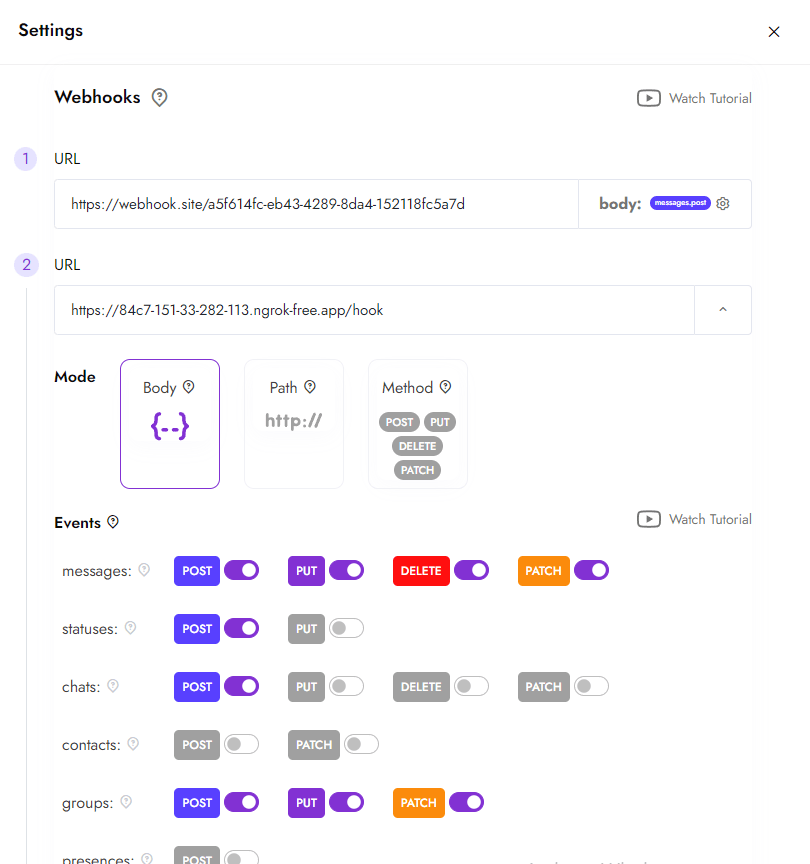
Configuración del webhook en el canal
- Vaya a la configuración del canal. En la página del canal, haga clic en el botón de configuración (en la esquina superior derecha).
- Configure el webhook. Especifique su URL en la sección de webhooks utilizando las configuraciones preseleccionadas. Puede configurar múltiples webhooks para diferentes eventos si es necesario. También puede cambiar estas configuraciones mediante la API.
- Guarde los cambios. Después de esto, todas las notificaciones sobre eventos en WhatsApp se enviarán al servidor que especificó.
Creación de la base del bot de WhatsApp en Python
Flask==3.0.0
requests==2.27.1
requests-toolbelt==0.9.1
python-dotenv==0.20.0pip install -r requirements.txtAPI_TOKEN=8FjpwmyFUulh7emXOprrET3xKrwJ984O # API token from your channel
API_URL=https://gate.whapi.cloud # API endpoint URL
PORT=80 # example, 80 or 443
#URL_LINK= The Webhook link to your server {link to server}/hook.from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
api_token = os.getenv("API_TOKEN")Envío de un mensaje de texto
import requests
# URL for sending text messages. Can be pulled from .env
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/text"
# Data for sending a message
payload = {
"to": "919984351847", # Enter the recipient's number in international format
"body": "Hello! This is a test message." # Text of message
}
# Headers, including authorization token
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": f"Bearer {api_token}" # Use the token from the .env file
}
# Sending a POST request
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
# Output server response
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
Recepción de mensajes a través de Flask Webhook
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
# Route for processing incoming messages
@app.route('/hook', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
# Retrieving data from a request
data = request.json
# Logging an incoming message
print("Received message:", data)
# Example of incoming message processing
if "messages" in data:
for message in data["messages"]:
sender = message["from"] # Sender's number
text = message.get("body", "") # Text of message
print(f"Message from {sender}: {text}")
# Logic for replying to a message
# Check out our examples on GitHub, where we use more branching on commands for the bot
if text.lower() == "hello":
send_response(sender, "Hi there! How can I help you?")
elif text.lower() == "bye":
send_response(sender, "Goodbye!")
return jsonify({"status": "success"}), 200
# Function for sending a reply
def send_response(to, body):
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/text"
payload = {
"to": to,
"body": body
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": f"Bearer {api_token}" # Use the token from the .env file
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(f"Response to {to}: {response.status_code}, {response.text}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
Funciones avanzadas
Envío de una imagen
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/image"
payload = {
"to": "919984351847",
"media": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/a9/Example.jpg",
"caption": "An example image"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
Envío de un archivo
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/document"
payload = {
"to": "919984351847",
"media": "data:application/pdf;base64,JVBERi0xLjQKJdPr6eEKMSAwIG9iago8PC9UaXRsZSAoVGVybXMgb2YgU2VydmljZSBXaGFwaS5DbG91ZCkKL0NyZWF0b3IgKE1vemlsbGEvNS4wIFwoV2luZG93cyBOVCAxMC4wOyBXaW42NDsgeDY0XCkgQXBwbGVXZWJLaXQvNTM3LjM2IFwoS0h............",
"filename": "Terms of Service Whapi.Cloud.pdf",
"caption": "Hello, I am attaching an important file to my message"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
Creación de un grupo de WhatsApp en Python
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/groups"
payload = {
"participants": ["919984351847", "919984351848", "919984351849"],
"subject": "Group Subject 3"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
Integración con ChatGPT: IA para tu bot de WhatsApp
Paso 1: Añadir dependencias de ChatGPT
openai>=1.91.0,<2.0.0
httpx>=0.28.1,<1.0.0
httpcore>=1.0.9,<2.0.0
- openai - el SDK oficial para enviar solicitudes a OpenAI y obtener respuestas de ChatGPT.
- httpx - una biblioteca moderna y asíncrona de cliente HTTP que openai usa internamente para realizar llamadas a la API.
- httpcore - una biblioteca de transporte de red de bajo nivel usada por httpx. Debe fijarse explícitamente para evitar conflictos de versiones.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Paso 2: Obtén tu clave API de OpenAI
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
Paso 3: Añadir la lógica de IA a tu bot
- - recibe eventos webhook entrantes de Whapi.Cloud,
- - detecta si el mensaje comienza con /ai,
- - envía la solicitud del usuario a ChatGPT mediante la API de OpenAI,
- - devuelve la respuesta generada por IA al usuario en WhatsApp.
# Import necessary libraries for web server, HTTP requests, OpenAI API, environment variables, and .env file loading
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify # Flask is used to create the web server and handle HTTP requests
import requests # Used to send HTTP requests to the WhatsApp API
from openai import OpenAI # OpenAI client for interacting with ChatGPT
import os # For accessing environment variables
from dotenv import load_dotenv # For loading variables from a .env file
# Load environment variables from a .env file into the environment
load_dotenv()
# Create a Flask web application instance
app = Flask(__name__)
# Retrieve required configuration values from environment variables
API_TOKEN = os.getenv("API_TOKEN") # Token for authenticating with WhatsApp API
API_URL = os.getenv("API_URL") # Base URL for WhatsApp API
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY") # API key for OpenAI
# Ensure all required environment variables are set, otherwise stop the program with an error
if not API_TOKEN or not API_URL or not OPENAI_API_KEY:
raise RuntimeError("Missing required environment variables: API_TOKEN, API_URL, or OPENAI_API_KEY")
# Initialize the OpenAI client with the provided API key
openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
# Function to send a prompt to ChatGPT and get a response
# Takes a string prompt and returns the model's reply as a string
def ask_openai(prompt):
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify which OpenAI model to use
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}] # Provide the user's message to the model
)
# Extract and return the text of the model's reply
return response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
# Function to send a text message to a WhatsApp user via the WhatsApp API
# 'to' is the recipient's chat ID, 'body' is the message text
def send_message(to, body):
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}", # Add authentication token to the request
"Content-Type": "application/json" # Specify that we're sending JSON data
}
payload = {"to": to, "body": body} # Prepare the message data
# Send the message to the WhatsApp API endpoint
response = requests.post(f"{API_URL}/messages/text", json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Whapi response:", response.status_code, response.text) # Log the API response for debugging
# Define a webhook endpoint to receive incoming WhatsApp messages
@app.route("/hook/messages", methods=["POST"])
def webhook():
data = request.json # Parse the incoming JSON data
print("Incoming:", data) # Log the incoming data for debugging
# Loop through all received messages (could be more than one in a single webhook call)
for msg in data.get("messages", []):
if msg.get("from_me"):
continue # Skip messages sent by the bot itself
sender = msg.get("chat_id") # Get the sender's chat ID
# Safely extract the message text, handling cases where 'text' might be missing
text = (msg.get("text") or {}).get("body", "").strip()
# If the message starts with '/ai ', treat it as a prompt for ChatGPT
if text.lower().startswith("/ai "):
prompt = text[4:].strip() # Extract the user's prompt after '/ai '
if not prompt:
send_message(sender, "Please provide a prompt after /ai.") # Ask user to provide a prompt
else:
try:
reply = ask_openai(prompt) # Get response from ChatGPT
send_message(sender, reply) # Send the response back to the user
except Exception as e:
send_message(sender, f"Error: {e}") # Inform user if something went wrong
else:
# If the message doesn't start with '/ai ', send instructions to the user
send_message(sender, "Hi! To ask me something, type:\n/ai your question")
# Respond to WhatsApp API to confirm receipt of the webhook
return jsonify({"status": "received"})
# Optional: health check endpoint to verify the bot is running
@app.route("/", methods=["GET"])
def index():
return "Bot is running"
# Function to register the webhook URL with the WhatsApp API
def register_webhook():
if os.getenv("BOT_URL"):
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}"}
payload = {
"webhooks": [
{
"url": os.getenv("BOT_URL"), # The public URL where Whapi should send messages
"events": [{"type": "messages", "method": "post"}], # Listen for message events
"mode": "method"
}
]
}
# Register the webhook
response = requests.patch(f"{API_URL}/settings", json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Webhook setup:", response.status_code, response.text) # Log the result
# If this script is run directly (not imported), start the bot
if __name__ == "__main__":
register_webhook() # Optionally register the webhook on startup
port = int(os.getenv("PORT", 80)) # Use the PORT environment variable or default to 80
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=port) # Start the Flask web server, accessible from any network interface
Solución de problemas
El bot no responde a mensajes entrantes
- Asegúrate de que estás enviando mensajes al número en el que se ejecuta el bot desde otro teléfono. El bot no podrá reaccionar a los mensajes enviados desde el mismo número.
- Si el bot no reacciona a los mensajes de otros números, verifica el funcionamiento de los webhooks. Utiliza servicios para simular webhooks, por ejemplo, Webhook.site, para asegurarte de por dónde llegan las solicitudes de callback. Luego, verifica que el camino coincide con lo que configuraste. Además, asegúrate de que tu servidor responde con 200Ok.
El bot envía mensajes sin parar
El bot funciona en algunos chats, pero en otros no
Despliegue y uso de servidores
Firebase
- Crea un proyecto en Firebase Console;
- Instala Firebase CLI, siguiendo las instrucciones;
- Inicializa Firebase en el directorio de tu proyecto con el comando firebase init;
- Despliega tu bot usando el comando firebase deploy --only functions.
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Regístrate o inicia sesión en AWS Management Console;
- Crea una nueva función Lambda a través de la consola de AWS, eligiendo API Gateway como desencadenante;
- Sube el código de tu bot a la función Lambda;
- Configura API Gateway para que tu bot interactúe con el mundo exterior.
Heroku
- Crea una cuenta en Heroku;
- Instala Heroku CLI e inicia sesión;
- Crea una nueva aplicación en Heroku a través de la consola o usando el comando heroku create;
- Conecta tu repositorio Git con Heroku y realiza el despliegue con los comandos git push heroku master;
- Configura la URL del webhook proporcionada por Heroku.