Python ile WhatsApp Otomasyonu
- Python kullanarak WhatsApp API ile nasıl çalışılır;
- Farklı görevleri otomatikleştirmek için Whapi.Cloud entegrasyonu;
- Mesajları işlemek ve otomatik yanıtlamak için webhook'ların kullanımı;
- WhatsApp botunuzu ChatGPT ile bağlayarak yapay zekâ destekli sohbetler gerçekleştirme;
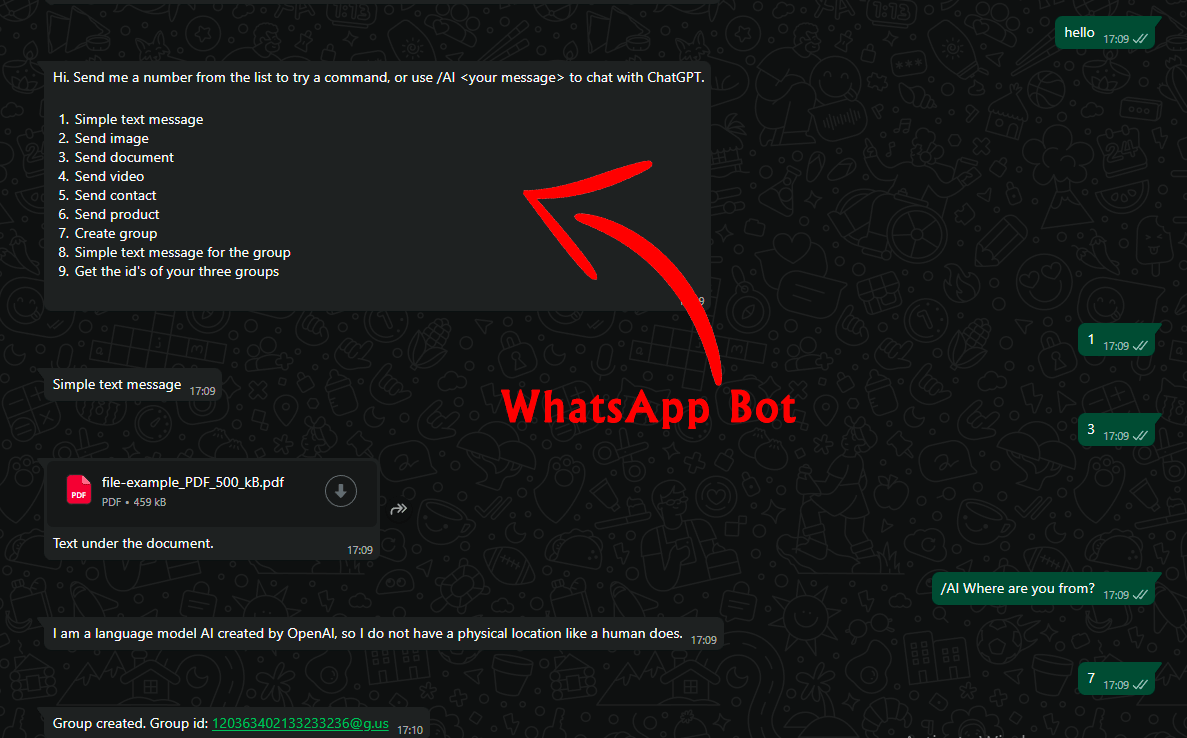
Ayrıca, işinizi kolaylaştırmak için GitHub'da yayınladığımız hazır Python bot scriptlerimizi kullanabilirsiniz. GitHub projelerimizde kurulum ve test süreçleri detaylıca açıklanmıştır ve kod içinde yararlı açıklamalar bulunmaktadır. Bu, yeni başlayan geliştiriciler için harika bir başlangıçtır.
Bot Geliştirme için Hazırlık
- Python. Python yüklü değilse kurun. En son sürümü (tercihen 3.6 veya üzeri) resmi web sitesinden indirin ve yönergeleri izleyin.
- Flask. Flask, hafif bir Python web framework'üdür ve sunucuyu kurmak ve webhook'ları işlemek için kullanılacaktır. Flask'ı şu komutla kurabilirsiniz: pip install Flask
- API Token. API token almak için Whapi.Cloud'a kaydolun. Bu token, botunuzun WhatsApp ile API üzerinden etkileşim kurmasına olanak tanır. Kayıttan sonra, bazı sınırlamalarla birlikte ücretsiz bir kanal sağlanacaktır. Bu, geliştirmenizi test etmek için yeterlidir. Whapi.Cloud, istikrarı, düşük maliyeti ve geniş özellikleri ile öne çıkan bir sağlayıcıdır. Token alımı ile ilgili talimatları aşağıda vereceğiz.
- Webhook Ayarı. Botun gelen mesajları ve WhatsApp'taki olayları işleyebilmesi için WhatsApp bildirimlerini işlemek üzere bir sunucu URL'sine (yerel veya harici) ihtiyacınız olacak. Bu bağlantının nasıl ve nereden alınacağı hakkında detayları makalemizde inceleyeceğiz.
WhatsApp API'si için Token Alma
Kayıt ve Numara Bağlama
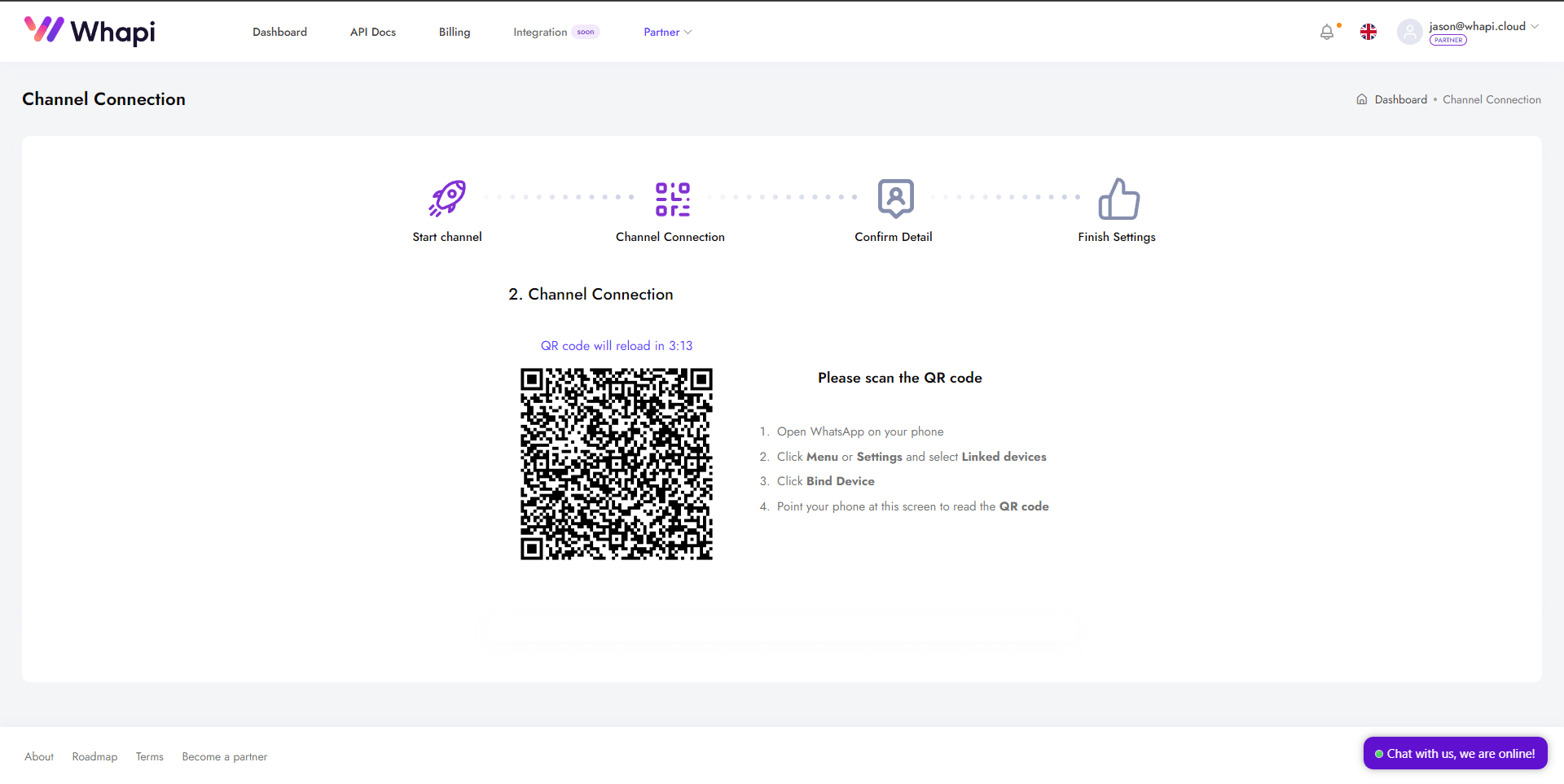
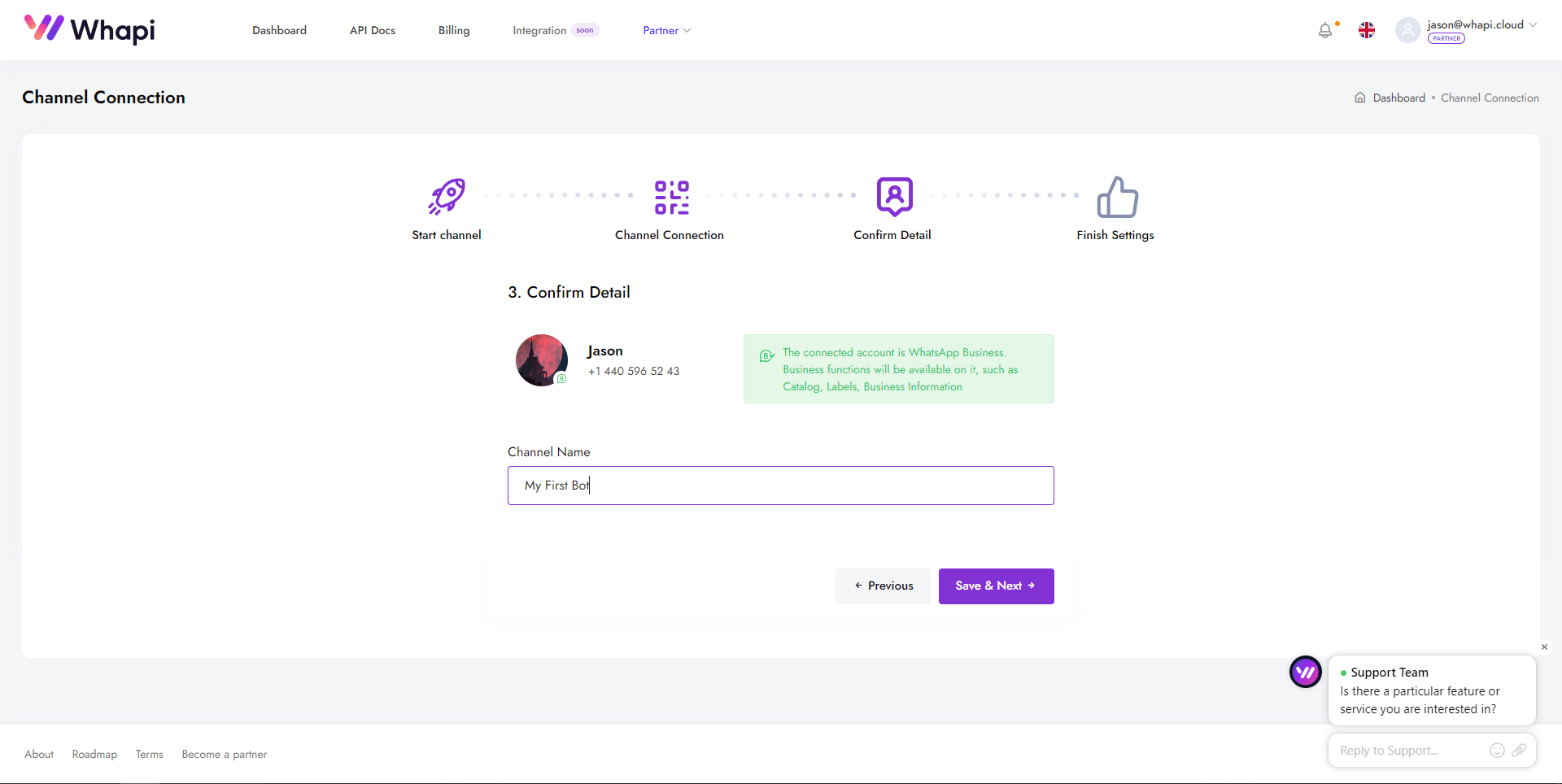
- 1. Kontrol paneline gidin ve sizin için önceden oluşturulmuş olan Default Channel sayfasını açın.
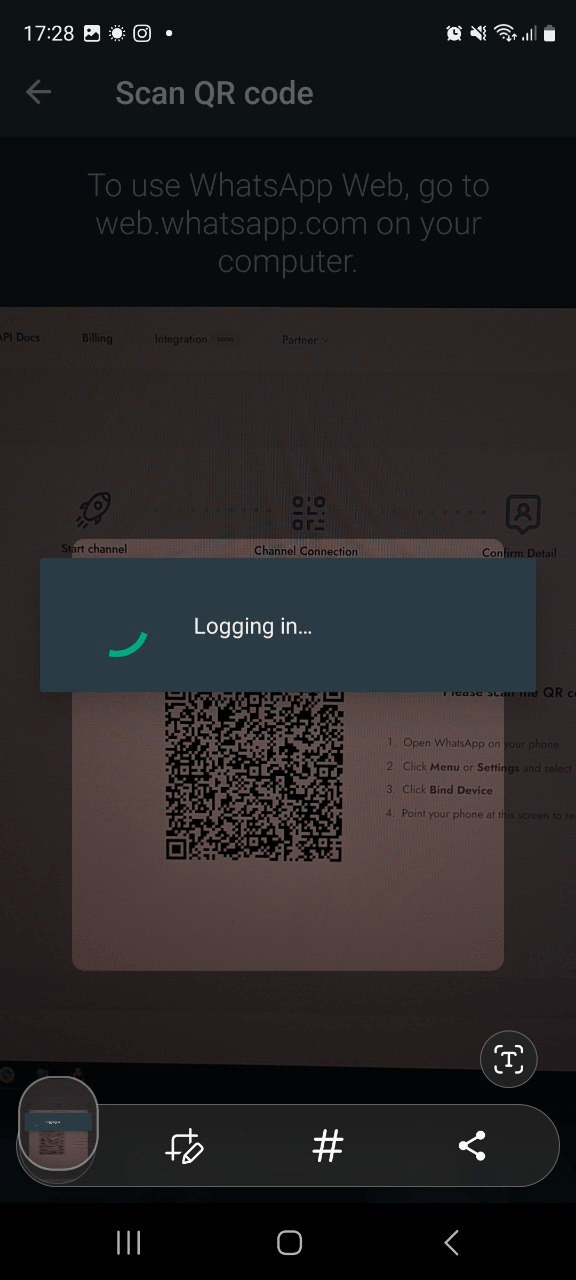
- 2. İlk adımda bir QR kodu ve talimatlar göreceksiniz.
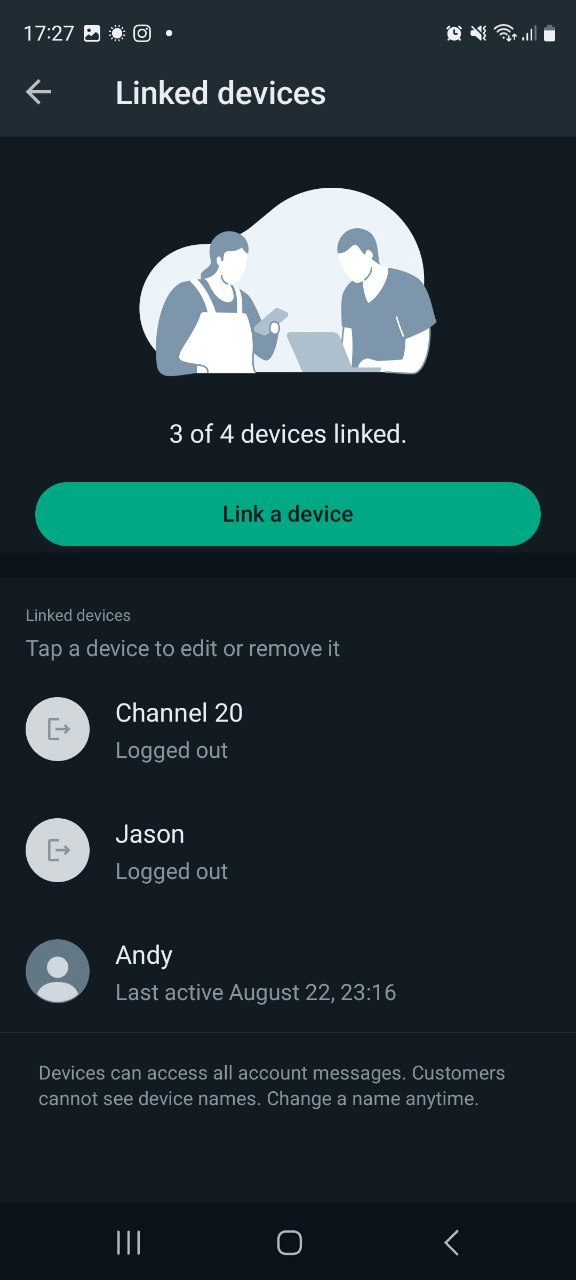
- 3. Cihazınızda WhatsApp'ı açın, Ayarlar → Bağlı cihazlar → Cihaz bağla → QR kodunu tara seçeneklerine gidin.
- 4. Başarılı bir bağlantıdan sonra, daha kolay çalışabilmek için kanala bir isim verin (örneğin, "Chatbotum").
API Token Alma
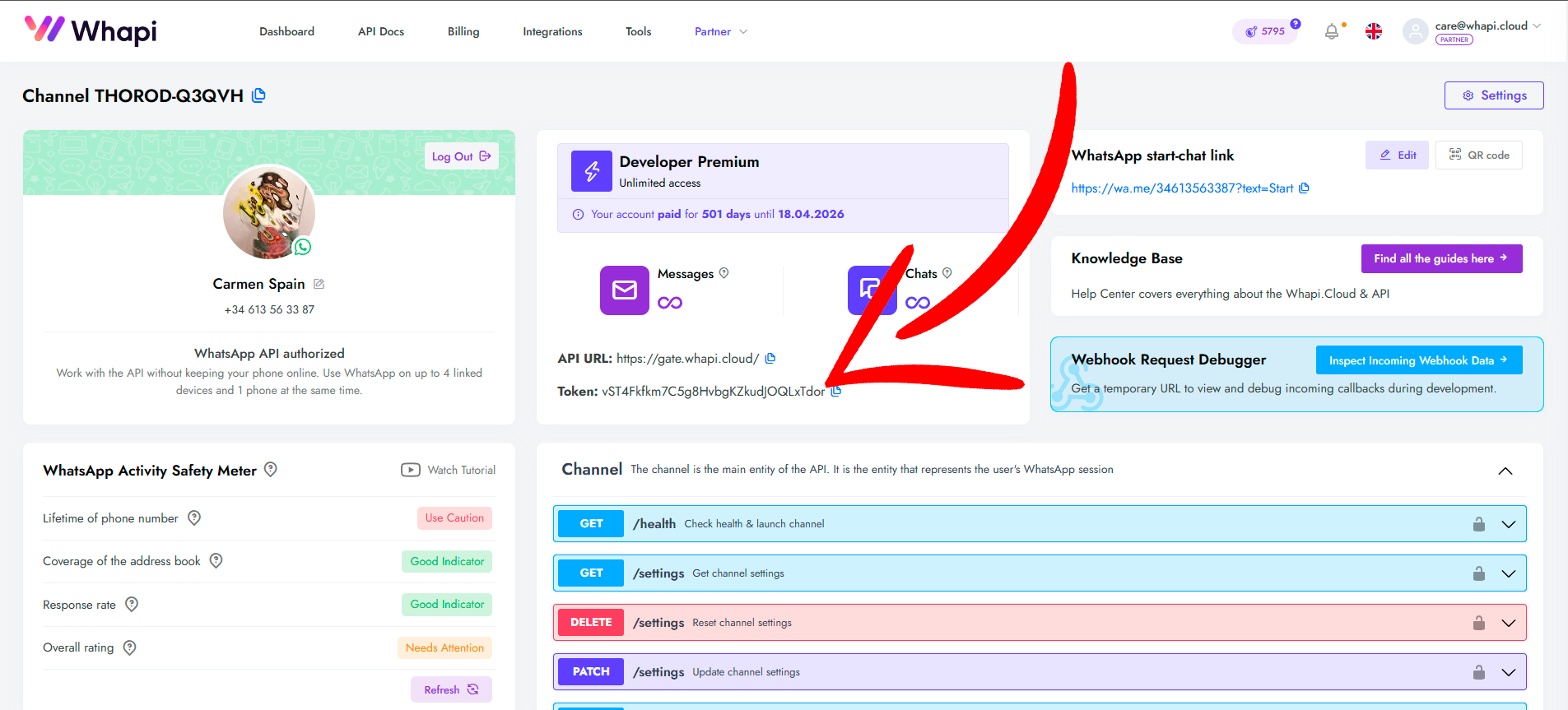 Your API Key
Your API Key
API ile Çalışma Araçları
- Geliştirici Merkezi: API uç noktalarına yönelik örnek kod parçaları almanıza olanak tanıyan belgeler ve örneklerle dolu özelleştirilmiş bir platform.
- Postman Koleksiyonu: API'yi Postman aracılığıyla test etmek için hazır istekler.
- Swagger Dosyası: Tüm API yöntemlerinin ayrıntılı bir açıklaması ve kanal sayfasında doğrudan test etme imkanı.
Webhook Nedir ve Nasıl Kurulur?
Webhook Nedir?
- Anlık bildirimler. Tüm olaylar neredeyse gerçek zamanlı olarak işlenir.
- Yüksek bant genişliği. Bildirim alma hızı yalnızca sunucunuzun performansı ile sınırlıdır.
- Esneklik. Sadece ihtiyacınız olan olayları alabilirsiniz, örneğin: Özel mesajlar; Grup mesajları; Mesaj durum değişiklikleri; Grup üyeleri değişiklikleri; Cevapsız çağrı bildirimleri; Kanal durumları ve daha fazlası.
Webhook URL'si Nasıl ve Nereden Alınır?
- 1) Ngrok'u resmi web sitesinden indirin ve çıkarın. Şimdi terminali açın ve Ngrok'un bulunduğu klasöre gidin.
- 2) ./ngrok http PORT_NUMARASI komutunu çalıştırın ve PORT_NUMARASI yerine Flask sunucunuzun yerel olarak çalıştığı portu (örneğin 80) yazın.
- 3) Artık webhook URL'si olarak kullanabileceğiniz bir genel URL'ye sahipsiniz. İleride kullanım için bu URL'yi kopyalayın.
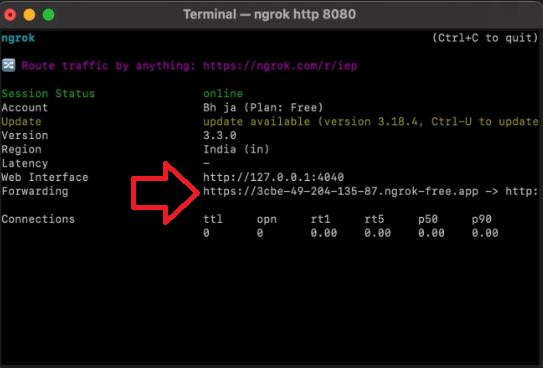
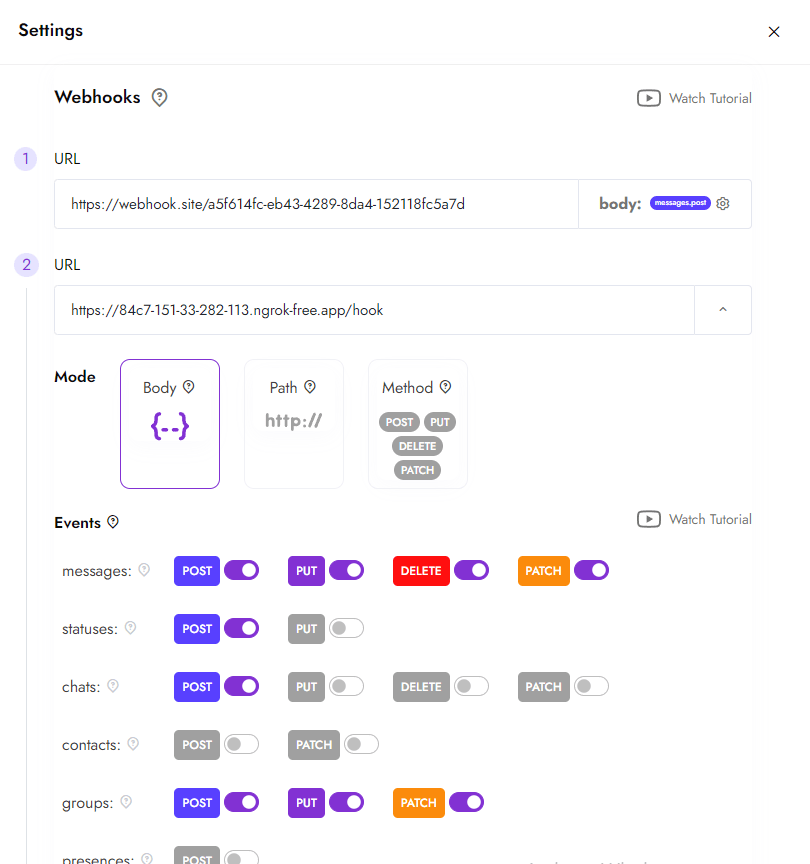
Kanalda Webhook Kurulumu
- Kanal ayarlarına gidin. Kanal sayfasında sağ üst köşedeki ayarlar düğmesine tıklayın.
- Webhook'u yapılandırın. Webhook bölümünde URL'nizi önceden seçilmiş ayarlarla girin. Gerekirse, farklı olaylar için birden fazla webhook ayarlayabilirsiniz. Ayrıca bu ayarları API aracılığıyla değiştirebilirsiniz.
- Değişiklikleri kaydedin. Bundan sonra WhatsApp'taki tüm olaylarla ilgili bildirimler, belirttiğiniz sunucuya gönderilecektir.
Python ile WhatsApp Botunun Temellerini Oluşturma
Flask==3.0.0
requests==2.27.1
requests-toolbelt==0.9.1
python-dotenv==0.20.0pip install -r requirements.txtAPI_TOKEN=8FjpwmyFUulh7emXOprrET3xKrwJ984O # API token from your channel
API_URL=https://gate.whapi.cloud # API endpoint URL
PORT=80 # example, 80 or 443
#URL_LINK= The Webhook link to your server {link to server}/hook.from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
api_token = os.getenv("API_TOKEN")Metin Mesajı Gönderme
import requests
# URL for sending text messages. Can be pulled from .env
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/text"
# Data for sending a message
payload = {
"to": "919984351847", # Enter the recipient's number in international format
"body": "Hello! This is a test message." # Text of message
}
# Headers, including authorization token
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": f"Bearer {api_token}" # Use the token from the .env file
}
# Sending a POST request
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
# Output server response
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
Flask Webhook ile Mesaj Alma
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
# Route for processing incoming messages
@app.route('/hook', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
# Retrieving data from a request
data = request.json
# Logging an incoming message
print("Received message:", data)
# Example of incoming message processing
if "messages" in data:
for message in data["messages"]:
sender = message["from"] # Sender's number
text = message.get("body", "") # Text of message
print(f"Message from {sender}: {text}")
# Logic for replying to a message
# Check out our examples on GitHub, where we use more branching on commands for the bot
if text.lower() == "hello":
send_response(sender, "Hi there! How can I help you?")
elif text.lower() == "bye":
send_response(sender, "Goodbye!")
return jsonify({"status": "success"}), 200
# Function for sending a reply
def send_response(to, body):
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/text"
payload = {
"to": to,
"body": body
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": f"Bearer {api_token}" # Use the token from the .env file
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(f"Response to {to}: {response.status_code}, {response.text}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
Gelişmiş Özellikler
Resim Gönderme
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/image"
payload = {
"to": "919984351847",
"media": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/a9/Example.jpg",
"caption": "An example image"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
Dosya Gönderme
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/messages/document"
payload = {
"to": "919984351847",
"media": "data:application/pdf;base64,JVBERi0xLjQKJdPr6eEKMSAwIG9iago8PC9UaXRsZSAoVGVybXMgb2YgU2VydmljZSBXaGFwaS5DbG91ZCkKL0NyZWF0b3IgKE1vemlsbGEvNS4wIFwoV2luZG93cyBOVCAxMC4wOyBXaW42NDsgeDY0XCkgQXBwbGVXZWJLaXQvNTM3LjM2IFwoS0h............",
"filename": "Terms of Service Whapi.Cloud.pdf",
"caption": "Hello, I am attaching an important file to my message"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
Python ile WhatsApp Grubu Oluşturma
import requests
url = "https://gate.whapi.cloud/groups"
payload = {
"participants": ["919984351847", "919984351848", "919984351849"],
"subject": "Group Subject 3"
}
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"content-type": "application/json",
"authorization": "Bearer Your_Token"
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
ChatGPT ile entegrasyon: WhatsApp botunuz için yapay zeka
Adım 1: ChatGPT Bağımlılıklarını Ekleyin
openai>=1.91.0,<2.0.0
httpx>=0.28.1,<1.0.0
httpcore>=1.0.9,<2.0.0
- openai - OpenAI’ye istek göndermek ve ChatGPT yanıtları almak için resmi SDK.
- httpx - OpenAI'nin dahili olarak API çağrıları için kullandığı modern, asenkron bir HTTP istemci kütüphanesi.
- httpcore - httpx tarafından kullanılan düşük seviyeli bir ağ taşıma kütüphanesi. Sürüm çakışmalarını önlemek için açıkça sabitlenmelidir.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Adım 2: OpenAI API Anahtarınızı Alın
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
Adım 3: Botunuza Yapay Zeka Mantığını Ekleyin
- - Whapi.Cloud’dan gelen webhook olaylarını alır,
- - mesajın /ai ile başlayıp başlamadığını algılar,
- - kullanıcının isteğini OpenAI API aracılığıyla ChatGPT’ye gönderir,
- - AI tarafından oluşturulan yanıtı WhatsApp üzerinden kullanıcıya iletir.
# Import necessary libraries for web server, HTTP requests, OpenAI API, environment variables, and .env file loading
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify # Flask is used to create the web server and handle HTTP requests
import requests # Used to send HTTP requests to the WhatsApp API
from openai import OpenAI # OpenAI client for interacting with ChatGPT
import os # For accessing environment variables
from dotenv import load_dotenv # For loading variables from a .env file
# Load environment variables from a .env file into the environment
load_dotenv()
# Create a Flask web application instance
app = Flask(__name__)
# Retrieve required configuration values from environment variables
API_TOKEN = os.getenv("API_TOKEN") # Token for authenticating with WhatsApp API
API_URL = os.getenv("API_URL") # Base URL for WhatsApp API
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY") # API key for OpenAI
# Ensure all required environment variables are set, otherwise stop the program with an error
if not API_TOKEN or not API_URL or not OPENAI_API_KEY:
raise RuntimeError("Missing required environment variables: API_TOKEN, API_URL, or OPENAI_API_KEY")
# Initialize the OpenAI client with the provided API key
openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
# Function to send a prompt to ChatGPT and get a response
# Takes a string prompt and returns the model's reply as a string
def ask_openai(prompt):
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify which OpenAI model to use
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}] # Provide the user's message to the model
)
# Extract and return the text of the model's reply
return response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
# Function to send a text message to a WhatsApp user via the WhatsApp API
# 'to' is the recipient's chat ID, 'body' is the message text
def send_message(to, body):
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}", # Add authentication token to the request
"Content-Type": "application/json" # Specify that we're sending JSON data
}
payload = {"to": to, "body": body} # Prepare the message data
# Send the message to the WhatsApp API endpoint
response = requests.post(f"{API_URL}/messages/text", json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Whapi response:", response.status_code, response.text) # Log the API response for debugging
# Define a webhook endpoint to receive incoming WhatsApp messages
@app.route("/hook/messages", methods=["POST"])
def webhook():
data = request.json # Parse the incoming JSON data
print("Incoming:", data) # Log the incoming data for debugging
# Loop through all received messages (could be more than one in a single webhook call)
for msg in data.get("messages", []):
if msg.get("from_me"):
continue # Skip messages sent by the bot itself
sender = msg.get("chat_id") # Get the sender's chat ID
# Safely extract the message text, handling cases where 'text' might be missing
text = (msg.get("text") or {}).get("body", "").strip()
# If the message starts with '/ai ', treat it as a prompt for ChatGPT
if text.lower().startswith("/ai "):
prompt = text[4:].strip() # Extract the user's prompt after '/ai '
if not prompt:
send_message(sender, "Please provide a prompt after /ai.") # Ask user to provide a prompt
else:
try:
reply = ask_openai(prompt) # Get response from ChatGPT
send_message(sender, reply) # Send the response back to the user
except Exception as e:
send_message(sender, f"Error: {e}") # Inform user if something went wrong
else:
# If the message doesn't start with '/ai ', send instructions to the user
send_message(sender, "Hi! To ask me something, type:\n/ai your question")
# Respond to WhatsApp API to confirm receipt of the webhook
return jsonify({"status": "received"})
# Optional: health check endpoint to verify the bot is running
@app.route("/", methods=["GET"])
def index():
return "Bot is running"
# Function to register the webhook URL with the WhatsApp API
def register_webhook():
if os.getenv("BOT_URL"):
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}"}
payload = {
"webhooks": [
{
"url": os.getenv("BOT_URL"), # The public URL where Whapi should send messages
"events": [{"type": "messages", "method": "post"}], # Listen for message events
"mode": "method"
}
]
}
# Register the webhook
response = requests.patch(f"{API_URL}/settings", json=payload, headers=headers)
print("Webhook setup:", response.status_code, response.text) # Log the result
# If this script is run directly (not imported), start the bot
if __name__ == "__main__":
register_webhook() # Optionally register the webhook on startup
port = int(os.getenv("PORT", 80)) # Use the PORT environment variable or default to 80
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=port) # Start the Flask web server, accessible from any network interface
Sorun Giderme
Bot Gelen Mesajlara Yanıt Vermiyor
- Botun çalıştırıldığı numaraya, başka bir telefondan mesaj gönderdiğinizden emin olun. Bot, aynı numaradan gönderilen mesajlara yanıt veremez.
- Eğer bot diğer numaralardan gelen mesajlara yanıt vermiyorsa, web kancalarının çalışıp çalışmadığını kontrol edin. Örneğin, Webhook.site gibi web kancası simülasyon servislerini kullanarak, geri çağırma isteklerinin hangi yoldan geldiğini doğrulayın. Daha sonra, yolun yapılandırmanızda belirttiğiniz yola uyup uymadığını kontrol edin. Ayrıca, sunucunuzun 200Ok yanıtı verdiğinden de emin olun.
Bot Durmaksızın Mesaj Gönderiyor
Bot Bazı Sohbetlerde Çalışıyor, Diğerlerinde Çalışmıyor
Dağıtım ve Sunucuları Kullanma
Firebase
- Firebase Console'da bir proje oluşturun;
- talimatları takip ederek Firebase CLI yükleyin;
- Proje dizininizde firebase init komutu ile Firebase'i başlatın;
- Botunuzu firebase deploy --only functions komutu kullanarak dağıtın.
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- AWS Yönetim Konsolu'na kaydolun veya giriş yapın;
- AWS konsolu üzerinden API Gateway tetikleyici olarak seçilerek yeni bir Lambda fonksiyonu oluşturun;
- Botunuzun kodunu Lambda fonksiyonuna yükleyin;
- Botunuzun dış dünya ile etkileşimde bulunması için API Gateway'i yapılandırın.
Heroku
- Heroku'da bir hesap oluşturun;
- Heroku CLI yükleyin ve sisteme giriş yapın;
- Konsol üzerinden veya heroku create komutunu kullanarak Heroku'da yeni bir uygulama oluşturun;
- Git reposunu Heroku ile ilişkilendirin ve git push heroku master komutları ile dağıtım yapın;
- Heroku tarafından sağlanan web kancası URL'sini ayarlayın.